Lesson 1
The Existing Banking System
How Blockchain does what Banks do
While this is not about Bitcoin, it is about Blockchain & there are different forms of Blockchain
Here we suggest to learn the Bitcoin form of Blockchain, as a basis for further education
It is our firm belief that investors will only appreciate the immense value of Distributed Ledger Technology, and the available investment options, by understanding the basics of Blockchain
Here we start with the current banking system and a series of simple transactions
The story continues as we morph into the new Blockchain model using simple concepts
The current banking system
Tom banks with Wells Fargo
Sue banks with Capital One
Walmart Banks with Bank of America
Tom & Sue each have $200 in their bank accounts
Tom buys a bike from Walmart for $100
Sue buys a coat from Walmart for $60
Sue send Tom a check for $30
Each bank “keeps track” of it’s client’s expenditures & balances
Consider if Wells Fargo acquires all the other banks
There is only 1 bank now & 1 ledger with all transactions
All transactions go through Wells Fargo
Lets add Bob, Jane and a few more transactions at Target
The software keeps track of how much money people have in their account
Replace Wells Fargo with 100 independent bookkeepers / verifiers
We send a copy of the ledger to all 100 verifiers
Every time there is a new transaction we send it to all 100 verifiers
Anyone can be a verifier, lets look at how they verify the transactions
Its really no different than the banking system
Instead of having many regulated banks, each with their own “centralized” ledgers we now have 1 ledger sent to many “decentralized” verifiers
Another name for Blockchain is DLT or Distributed Ledger Technology
Verification of transactions
Sam is a verifier
The Ledger is split into blocks of transactions
In this case its 2 transactions per block but it could be 3 or more transactions per block, typically less than 10
Sam verifies & signs block 1, Fred verifies & signs block 2, Lucy verifies & signs block 3
We explain below how its verified & signed
Once a block is verified & signed it is copied to all 100 independent verifiers and it cannot be changed unless all 100 got together to commit fraud. It’s immutable
Bitcoin verifiers are also called “miners”, they receive a reward for verifying 1 block, currently 2.5 Bitcoin ! This is how new Bitcoins are mined into the system
This is similar to a gold miner being rewarded for finding new gold
The reader could stop here, you now have the basics of using a blockchain to keep track of financial transactions, just like a bank does but using distributed verifiers and a distributed common ledger of transactions
However, the magic is explained below, how we use encryption or cryptography to prevent fraud and guarantee the integrity of the system
It seems complex at first, it’s very different, but after a while it becomes easy and obvious
You may have questions:
Q: How do the transactions get done without a bank or credit / debit card and sent to miners for verification ?
A: Everyone in the system uses the same open source software, perhaps you use the Coinbase App, or similar to buy bitcoin with $, and you want to buy something with your bitcoin (many places now accept bitcoin), you simply open your Coinbase app, type in the name of the person to send the bitcoin to and click send, the transaction copy gets sent to every miner in the system so they can begin verifying the transaction
Q : I thought we don’t use real person names in crypto ?
A: Correct, this page is a simplified version. In the real transaction everyone has their own crypto ID, they call it a Key, basically a secure user name to identify you are who you say you are. (See advanced education Private Key - Public Key)
Q: How do we trust the validity of the transaction with these random “miners” in the way we trust the banks currently ?
A: This is the key question, lets break down the steps:
Transaction SEND: Person A from a phone / Coinbase APP sends 1 bitcoin (1 btc) to Store B ( A & B have a unique KEY, a very long user ID containing letters & numbers). TRANSACTION [A pays B 1btc]
Transaction VERIFY: The Coinbase App is part of the Open Source Bitcoin system, open source means thousands of independent programmers can check its working normally. The verifiers (MINERS) all get a copy of this transaction.
For the SEND, think of the old paper checks we used to write, we put our signature on the check and if there were any changes you had to sign your initials to say you made the change. If a check had something crossed out and replaced, but no signature or initials, then the bank rejects the transaction
The digital SEND is similar, the Coinbase APP, using person A’s private KEY, signs the transaction with the key. The key is as unique as the persons old paper signature. We now have [A pays B 1btc-signed by A], this is now encrypted and sent to all the miners.
The miner’s bitcoin software decrypts the transaction, the method of encryption-decryption used guarantees that A & B are who they say they are and the transaction has not been modified by any hackers along the way. For example, if a hacker changed 1btc to 2btc then the miners decryption software will only show a signature if no changes were made to the original transaction, so [A pays B 1btc-signed by A] is normal but [A pays B 2btc————-] has no signature so is invalid, just like a paper check with a number crossed out and changed but no initial.
We will add advanced education to this site for those interested in how the encryption-decryption software actually does what is described above. This is the essence of why blockchain works, a digital signature using a unique user ID (key) that guarantees that the original transaction is transmitted correctly and correctly entered into the books.
Q: How do we trust the miners to not modify transactions ?
A: There are over 1m bitcoin miners in the world, normal people with a normal computer, anyone can be a miner, you can use your current laptop. Similar to the encryption above to prove the transaction itself is valid, we use similar encryption to prove a miner made no changes to any transactions. If they did it would show up in the system that someone made a change and would be invalidated. 1m miners can’t all be crooked. The following section explains how the miners do the validation and we show 1 crooked miner and how it gets detected and rejected.
The following is a bit advanced but is a good first step to understand the power of how we can switch from banks to individuals to verify financial transactions.
Verify Block 1 / Encryption a.k.a. Cryptography
We do this one block at a time
Every Verifier is working on Block 1, its a race to be first to verify it and get paid 2.5 BTC
The word “crypto” is often used
It means enCRYPTion, we are going to verify using a type of encryption
Encryption is a “rule” to modify words then using the same rule we de-crypt or de-modify the words.
A simple example is a “rule” to “add 1 letter”, so the word HELLO becomes encrypted to IFMMP, simply adding 1 letter, H becomes I, E becomes F & so forth. The rule could be more complex like adding 3 letters. As long as the rule, or “Key”, is known by both parties, we can encrypt and de-crypt
There is an existing mathematical encryption rule called SHA 256, also known as “Hashing”. It’s slightly different in that its a 1-way encryption, it can’t be de-crypted
Go to any Hashing website like: https://www.miraclesalad.com/webtools/sha256.php
Type / paste this string exactly: Tom buys bike from Walmart 100
Look at the Hash, its: 21b675a69bea6c4f378e70714b4b8fc63f196b79d57aa650d13cddf4890011de
Its basically a code that uniquely represents the exact words in the string, make any change to the string and the Hash changes
Lets make a small change, simply add a “period” at the end of the string Tom buys bike from Walmart 100.
Notice the Hash is now completely different, just by adding a “period”
now remove the “period” the hash goes back to 21b675a69bea6c4f378e70714b4b8fc63f196b79d57aa650d13cddf4890011de
Same as before. The Hash is a unique “fingerprint” of the words, the letters & numbers
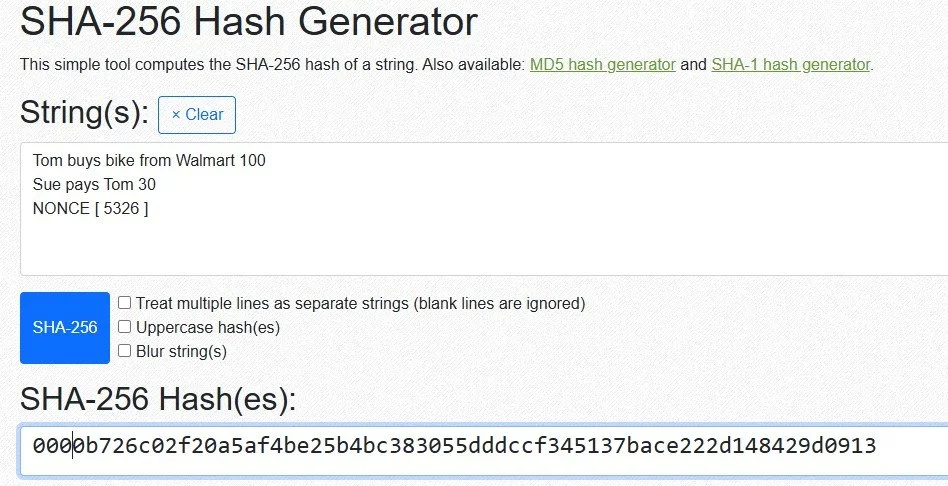
Now type the entire block 1 transaction data into the string to be Hashed:
Tom buys bike from Walmart 100 Sue pays Tom 30
A new Hash is generated ca800297a12a689353592807dbb906b99f3dba98d7f25edcbd0268bbd7832e58
There is another piece of data we need to add to the block
It’s called a NONCE, its the Verifier’s computer guessing a number - literally
Here we guess: 3001
This “3001” is “extra” data in the transaction so it causes a different Hash
The verifier’s (miner’s) computer keeps guessing different numbers, 3002, 3003 etc. until the hash begins with four zeros, 0000 _ _ _ _
This is the Bitcoin rule to “verify” the transaction
Bitcoin Miners buy computers with high hash rates to do this quickly
Once a miner generates a hash beginning 0000 then the block is verified - it’s only as crazy as digging a hole looking for gold !
Here we see on Sam’s computer, after many false guesses, the NONCE is finally [ 5326 ] and the Hash is 0000b726c02f20a5af4be25b4bc383055dddccf345137bace222d148429d0913
The Block is verified
Lets represent this in a simpler graphic
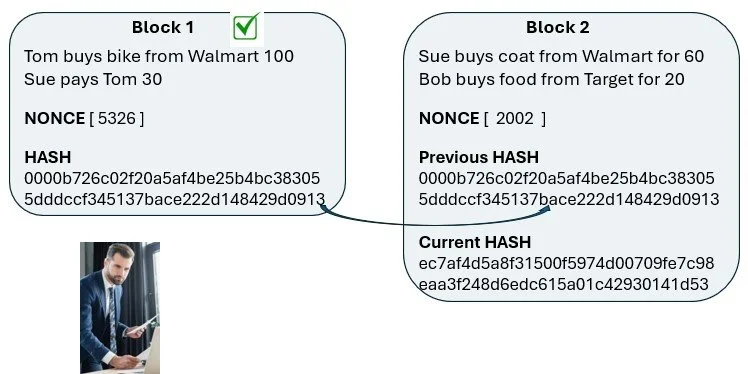
Here we see Block 1 with a Nonce of 5326 that generated a Hash beginning with 0000, block is now verified. Block 1 was mined by Sam
Block 2 is getting closer to how this looks in reality, the Hash from Block 1 is copied to Block 2 “previous hash”
Block 2 has its own transaction data, a place to guess a Nonce and now has the prior Hash as part of the data of Block 2
All the data in a block, the transaction data, the Nonce & the prior Hash all contribute to the Hash of that block
Block 1 is now “verified & signed” because the Hash begins with 0000 and the Hash is sent to Block 2
All the Miners now focus on Block 2 and start guessing the Nonce
Here Block 2 is Mined by Fred, verified & signed
The 0000 Hash of Block 2 will be sent to Block 3
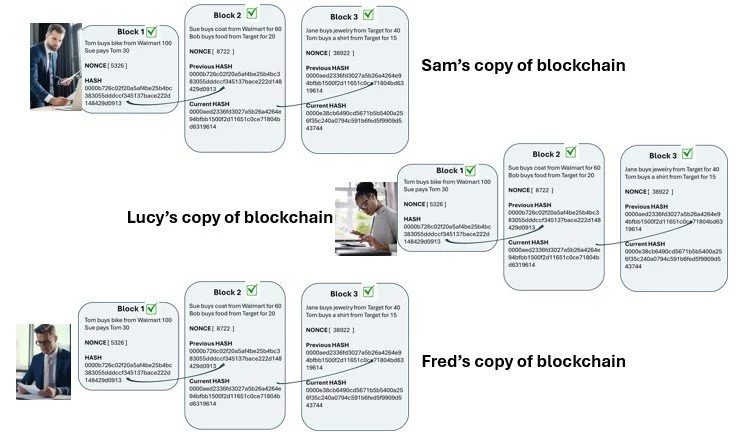
Here are the 3 blocks, all mined successfully
Notice we only see Sam now
While the other blocks were mined by other miners, every miner simply gets the updated blockchain
In this case we are looking at Sam’s version of the blockchain
Fred & Lucy are looking at their own version, it’s the same
Here we see all 3 miners
They all have the exact same copy of the blockchain
This is normal
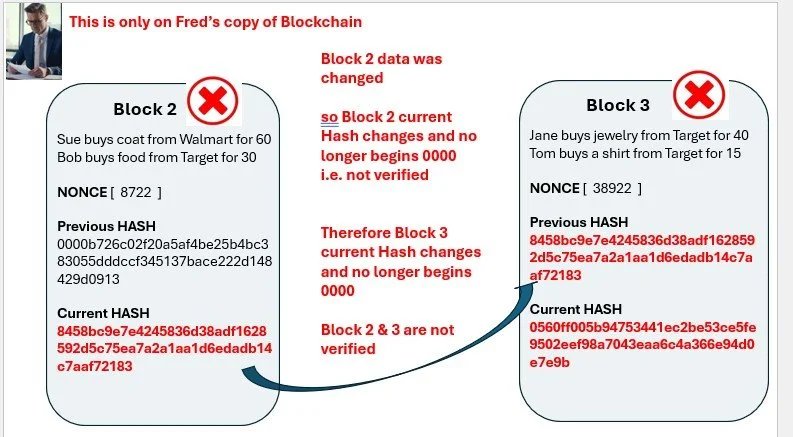
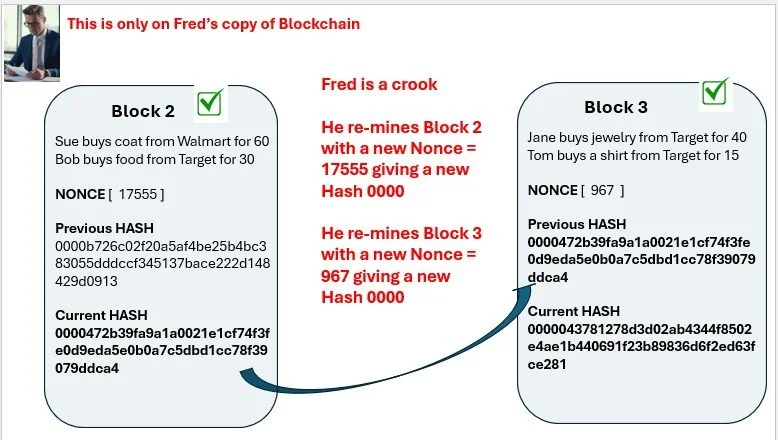
Fred is a crook, he changes Block 2: $20 to $30
Here we see the old & new Block 2 on Fred’s copy of the Blockchain
Fred’s copy of Block 2 , the data is now different
The Hash changed because the data changed
The new Hash does not begin 0000 so Fred’s copy of Block 2 is not verified
The new Hash in Block 2 flows to Block 3
So the data in Block 3 changes as the Previous Hash changed
So the Current Hash of Block 3 is different and does not begin 0000
Block 3 is now not verified
all this is only in Fred’s copy of the Blockchain
There is no impact to the other Miners copy of the Blockchain
Fred the crook now RE-MINES Block 2
He finds a new NONCE = 17555 for Block 2 that gives a Hash beginning with 0000 and Block 2 is now verified again
This new Hash flows to Block 3 where Fred RE-MINES and finds a Hash = 967 that gives a Hash beginning with 0000 and Block 3 is verified again
Fred thinks he has got away with his fraud, his Blockchain copy is all check marks - looks good
Recall, all that Fred did is only on his copy of the Blockchain
Lets look at all the copies of the Blockchain, Fred, Lucy & Sam
We only need to look at the last Block in the chain, in this case Block 3
Recall Fred made changes that mean his “Current Hash” in the last Block is diferent than Sam & Lucy’s versions, theirs are identical
Blockchain is a democracy, Lucy & Sam win 2:1
Fred’s version is rejected
The Blockchain continues without Fred’s data
There are over 1m miners
Mostly independent of each other
Its easy to become a miner
It would take 500,001 miners to collaborate to commit fraud
The data is therefore immutable
Once verified it cannot be changed